Magnetic Dipole
Magnetic Dipole Assignment Help | Magnetic Dipole Homework Help
Magnetic Dipole
A system consisting of two opposite magnetic poles at a small distance apart is called a magnetic dipole. Short bar magnets, compass needles, current loops, current carrying coils, solenoids etc., may be regarded as examples.(i) There are two types of magnetic charges, positive magnetic charge and negative magnetic charge. A magnetic charge p placed in a magnetic field B experiences a force
F = pB … (1)
The force on a positive magnetic charge is along the field and the force on a negative magnetic charge is opposite to the field.(ii) A magnetic charge p produces a magnetic field
B = μ0/4π p/r2 … (2)
at a distance r from it. The field is radially outward if the magnetic charge is positive and is inward if it is negative.(iii) A magnetic dipole is formed when a negative magnetic charge – p and a positive magnetic charge +p are placed at a small separation d.
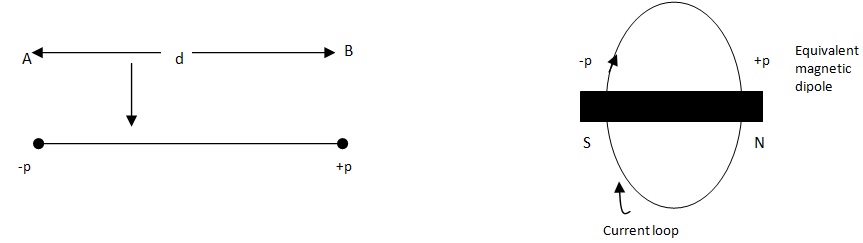
The magnetic dipole moment is m = pd.
Its direction is from –p to +p.
The line joining –p and +p is called the axis of the dipole.
(iv) A current loop of area A carrying a current I may be replaced by a magnetic dipole of dipole moments m = pd = iA placed along the axis of the loop.
We call a positive magnetic charge a north pole (N) and a negative magnetic charge a south pole (S).
The quantity p is called pole strength.
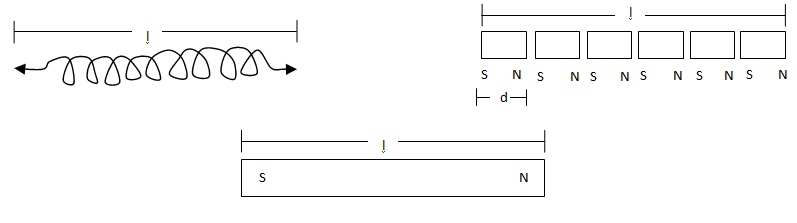
(v) A solenoid very closely resembles a combination of circular loops placed side by side.
Let i be the current through the solenoid and A be the area of cross-section. Dipole moment of each turn is m = i/A.
Each turn may be replaced by a small dipole placed at the centre of the loop along its axis. Suppose, each turn is replaced by a magnetic dipole with pole strength p and separation d between the north and south poles. We have pd = iA.
Suppose we take the value of d in such a way that the north pole of one dipole touches the south pole of the adjacent one. South poles and north poles, then, neutralize each other except at the ends. Thus, a current-carrying solenoid can be replaced by just a single south pole and a single north pole of pole strength p each, placed at a separation equal to the length of the solenoid.
For more help in Magnetic Dipole click the button below to submit your homework assignment.