Factors Affecting Organization Structure
Factors Affecting Organization Structure Assignment Help | Factors Affecting Organization Structure Homework Help
Factors Affecting Organization Structure
Organization structure is designed keeping in view the following factors:1. Strategy:
Strategy determines a course of action to direct various organizational activities. It makes plans to co-ordinate human and physical resources to work towards a common objective. Strategy is pre-requisite to organization structure and also follows it. The relationship between strategy and organization structure is depicted as follows: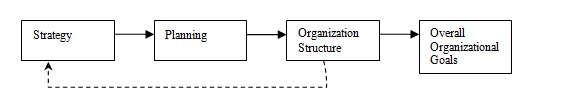
Strategies to diversify product lines or markets require decentralized transition as decision-making is done at wider level and strategies for organizations working in stable environment. Where managers do not diversify their operations, require a centralized organization.
2. Technology :
The technology for manufacturing goods and services also affects the organization stricture.In case of mass production technology, mechanistic organization structure is more appropriate, while in case of continuous production or small scale production technology, the appropriate from is organic structure. This is because mass production technologies involve standardization and specialization of work activities and continuous or unit production technologies require low levels of standardization and specialization.
3. People:
Organization structure defines work, groups it into departments and appoints people to run those departments. People at different jobs must possess the skill, knowledge and efficiency to accomplish the related tasks.4. Tasks :
Activities performed by people who transform organizational plans into reality are known as tasks. Various task characteristics are:(a) Skill variety:
It is the extent to which creativity and variety of skills and talents are required to do a task.People with high degree of task varieties (for example, a dress designer ) perform tasks that increase their intellectual ability and give them high job satisfaction.
(b) Task identity:
Whether to produce a product in whole or in parts determines its task identity. When a product is produced as a whole, it has greater task identity.People performing tasks with high task identity y (for example, a computer programmer) perform various job functions related to that task from beginning to the end, derive job satisfaction out of their work and feel motivated to repeat those tasks.
(c) Task significance:
The importance of task affecting the well-being or lives of people working inside and outside the organization determines significance of the task.People performing tasks with high task significance, i.e., tasks which positively affect the well-being and safety of others (for example, a traffic police inspector), feel satisfied with their job performance and perform work of high quality and esteem.
(d) Autonomy:
Whether or not an individual plans the task on his own determines autonomy ofthe task.
It determines the extent to which a person enjoys t freedom of performing various
Job activities and determines the steps or procedures to carry them out. People who are responsible for all the functions and schedules related to a job (for example, a project manager) hold accountability for that job and enjoy greater autonomy with respect to that task and derive greater job satisfaction.
(e) Feedback:
It is the information that people receive about successful completion of their task.5. Decisions:
Questions like who makes decisions-top managers or lower level managers, how information flows in the organization so that decision-making is facilitated, affect the organization structure.
Centralized decision-making powers give rise to mechanistic structures and decentralized decision-making processed give rise to organic or behavioral structures.
6. Informal organization:
Informal organizations are and outgrowth of formal organizations. Social and cultural values, religious beliefs and personal likes and dislikes of members which form informal groups cannot be overlooked by management.7. Size:
A group known as Aston Group conducted research on firms of different sizes and concluded that as firms increase in size, the need for job specialization, standardization and decentralization also increases and organizations are structured accordingly.8. Environment:
Organization structure cannot ignore the effects of environment. Organizations must adapt to the environment, respond to incremental opportunities and satisfy various external parties such as customers, suppliers, layout unions etc.In case of stable environment where people perform routine and specialized jobs, which do not change frequently, a closed or mechanistic organization structure is appropriate.
9. Managerial perceptions:
Organizations where top managers perceive their subordinated as active, dynamic and talented entrepreneurs, prefer organic form of structure, If they hold negative opinion about their subordinates, they prefer mechanistic organization structure.For more help in Factors Affecting Organization Structure click the button below to submit your homework assignment